Blog: Wired vs. Wireless Conference Room Phones
What are the Pros & Cons of Wired and Wireless Conference Room Phones
In the world of telecommunications, conference phones are essential tools for effective business communication. They help facilitate meetings, discussions, and decision-making processes, ensuring smooth operations and collaboration among team members. As technology advances, two types of conference room phones have emerged: wired and wireless. In this Metropark blog post, we will delve into the differences between these two types, highlighting their features, pros, and cons, to help you determine which one is best suited for your business needs.
Wired Conference Room Phones
Wired conference room phones, such as the CP960 from Metropark, connect to the internet via an Ethernet cable. This connection ensures a stable and reliable network, which translates into better sound quality and fewer interruptions. The wired connection also provides a consistent power supply, ensuring that the phone remains on and functional even during power outages.
Pros:
- Stable and reliable connection: The Ethernet cable connection ensures a stable and consistent network, leading to better sound quality and fewer interruptions.
- High-quality audio: Wired conference room phones often have high-quality microphones and speakers, resulting in clear audio during meetings.
- Consistent power supply: A wired connection provides a reliable power source, ensuring that the phone remains on and functional even during power glitches.
Cons:
- Limited placement options: The need for an Ethernet cable connection may limit the placement options for the phone, potentially affecting the acoustics of the meeting room.
- Cable management: Managing and organizing the Ethernet cable can be a hassle, especially in large conference rooms.
- Potential for cable damage: The Ethernet cable can be accidentally tripped over or damaged, leading to connectivity issues.
Wireless Conference Room Phones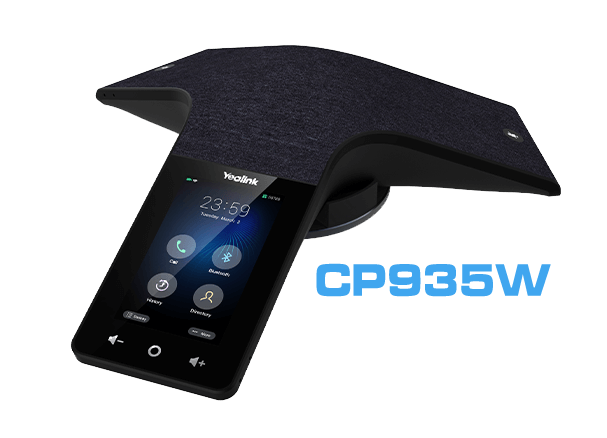
Wireless conference room phones, like the CP935W from Metropark, operate without the need for an Ethernet cable. This type of phone connects to the internet via DECT back to a base unit, providing greater flexibility in terms of placement and mobility. Wireless conference room phones often come with rechargeable batteries, allowing for extended usage without the need for constant charging.
Pros:
- Flexibility and mobility: Wireless conference room phones can be easily moved and placed anywhere within the DECT or WI-FI range, providing greater flexibility in terms of meeting room layout and acoustics.
- Easy setup: Wireless conference room phones do not require the installation of Ethernet cables, making setup and installation a breeze.
- Aesthetically pleasing: The absence of cables provides a cleaner and more visually appealing conference room setup.
Cons:
- Dependence on DECT or Wi-Fi: The reliability of wireless conference room phones is dependent on the strength and stability of the DECT or Wi-Fi connection.
- Battery life: Wireless conference room phones rely on rechargeable batteries, which may need to be charged frequently, depending on usage.
- Potential for interference: Wireless DECT or Wi-Fi signals can be affected by interference from other wireless devices, potentially leading to intermittent audio quality during meetings.
In conclusion, both wired and wireless conference room phones have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Wired conference room phones offer a stable and reliable connection, high-quality audio, and a consistent power supply. However, they may have limited placement options and require cable management. On the other hand, wireless conference room phones provide flexibility and mobility, easy setup, and an aesthetically pleasing conference room setup. However, they depend on DECT or Wi-Fi, have battery life considerations, and may be affected by interference. Ultimately, the choice between wired and wireless conference room phones depends on your specific business needs, meeting room layout, and preferences.